A Technical SEO audit is an essential step for improving your website’s search engine visibility and ensuring a smooth user experience. By identifying and fixing technical issues, you can enhance your site’s performance, user experience, and overall ranking. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive Technical SEO audit:
1. Crawl Your Website
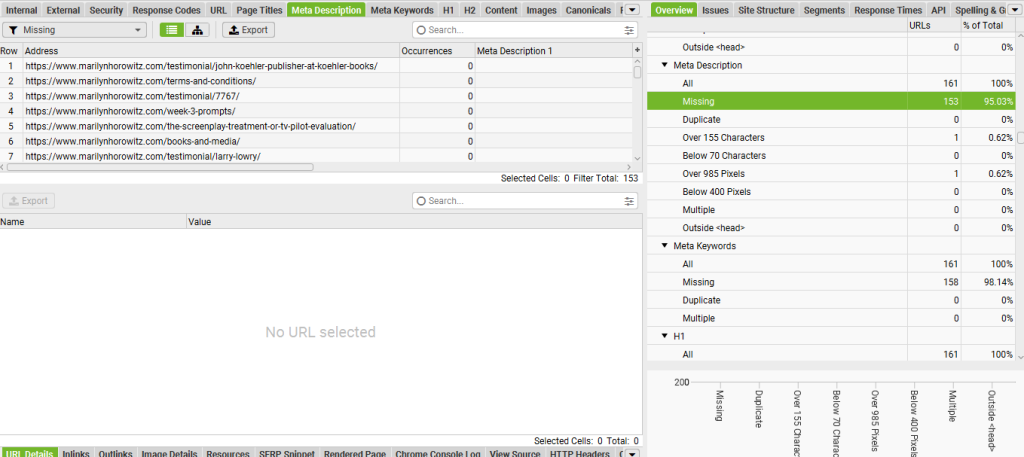
The first step in any SEO audit is to crawl your website. This helps you identify issues such as broken links, duplicate content, and other technical problems. Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or Sitebulb to crawl your website and gather data.
Key points to look for:
- Crawl Errors: Check for 404 errors or broken links.
- Redirects: Identify unnecessary or incorrect redirects (e.g., 301 or 302 status codes).
- Duplicate Content: Look for duplicate pages or content that could harm SEO.
2. Check Website Speed and Performance
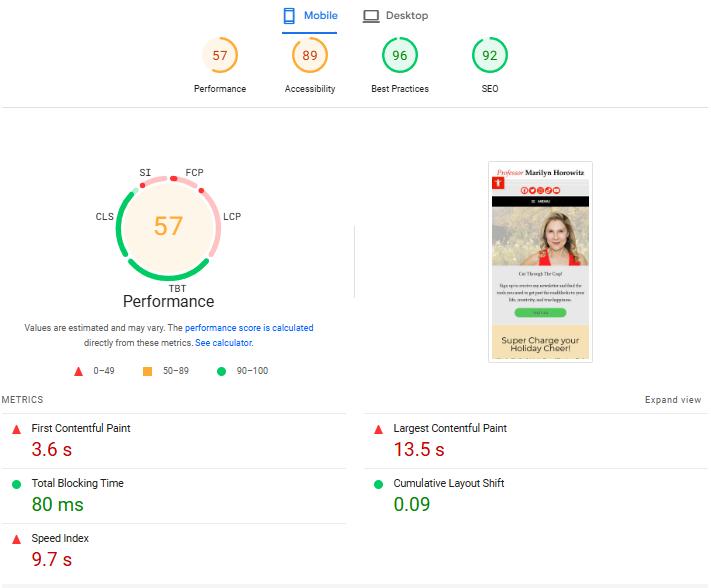
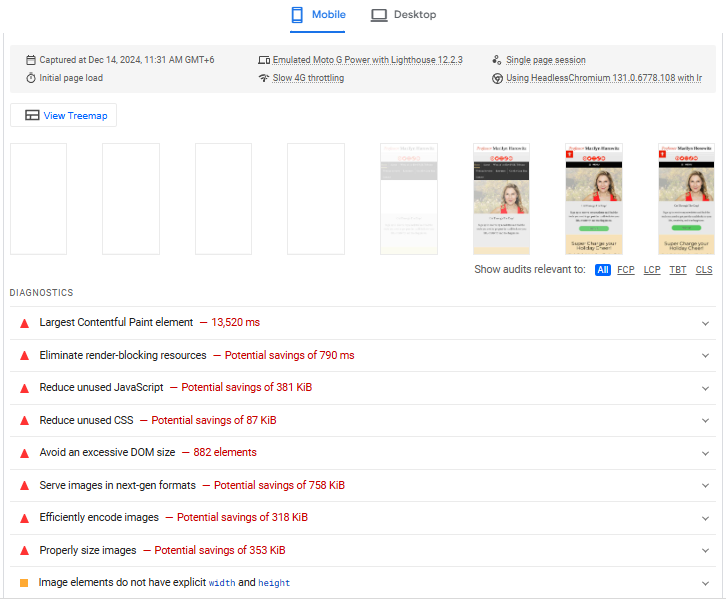
Page load speed is a critical ranking factor for search engines, as well as for user experience. Slow-loading pages lead to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. Use Google PageSpeed Insights, GTMetrix, or Lighthouse to evaluate page speed.
Key metrics to assess:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Measures the time it takes for content to appear on screen.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How long it takes for the largest visible element to load.
- Total Blocking Time (TBT): How long your page remains unresponsive during loading.
Make adjustments based on suggestions to improve load speed, such as optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and reducing JavaScript bloat.
3. Mobile friendliness check
With mobile-first indexing, Google now prioritizes the mobile version of your website for ranking. Make sure your site is fully responsive and optimized for mobile devices.
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to check your site’s mobile performance. Ensure:
- Responsive design (adapts to screen sizes)
- Easy navigation on smaller screens
- Optimized touch elements and buttons
4. Examine Website Structure and Navigation
Website structure plays an important role in both SEO and user experience. Ensure your site is well-organized, with clear categories, and easy navigation for both users and search engines.
Things to check:
- URL Structure: URLs should be short, descriptive, and include relevant keywords.
- Internal Linking: Ensure that key pages are properly interlinked to spread link equity.
- Sitemap: Check if you have an XML sitemap and that it’s submitted to Google Search Console.
5. Review Robots.txt and Meta Robots Tags
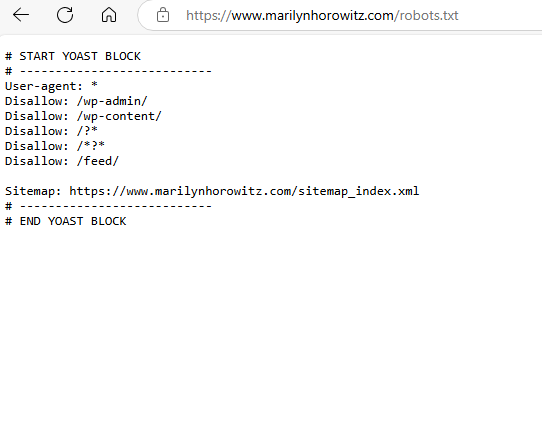
The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages to crawl or not to crawl. A misconfigured robots.txt file could block important pages from being indexed.
Ensure:
- Your robots.txt file is not blocking important resources (e.g., CSS, JS).
- You’re not accidentally preventing pages from being crawled using “noindex” or “nofollow” meta tags.
6. Check for Broken Links
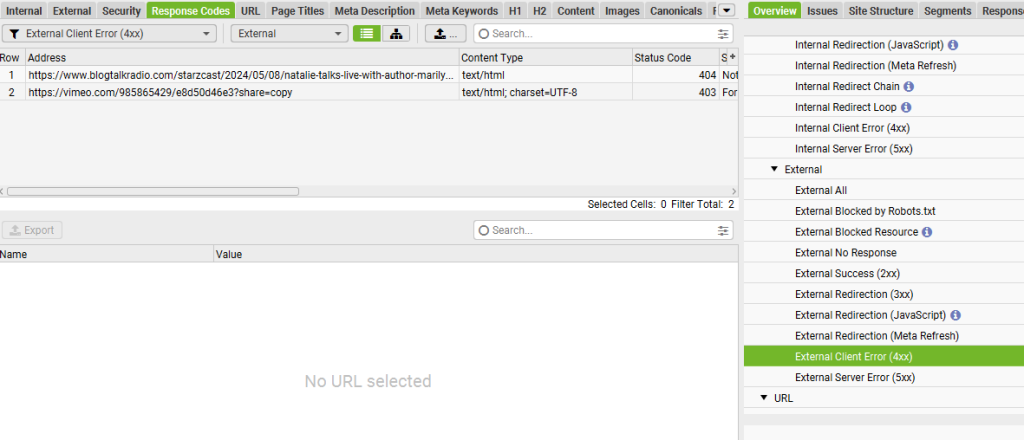
Broken internal and external links can harm your site’s SEO. They create a poor user experience and signal to search engines that the site is not well-maintained. Use crawling tools like Screaming Frog to find and fix broken links.
7. Analyze Backlink Profile
Backlinks are one of the most important ranking factors in SEO. Analyzing your backlink profile helps you identify toxic or low-quality links, as well as opportunities for improvement.
Use tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or SEMrush to analyze backlinks. Look for:
- Toxic or spammy backlinks: These can negatively impact your rankings. Disavow low-quality links if necessary.
- Link opportunities: Identify websites with high domain authority for future link-building campaigns.
8. Optimize for Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of user experience metrics introduced by Google that measure the performance of your website. These include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Use Google Search Console to track these metrics and address any issues that may affect user experience.
9. Check for HTTPS Security
Security is essential for both user trust and SEO. Google gives preference to websites with HTTPS encryption. Ensure your website is using a valid SSL certificate.
Check if:
- All pages are served over HTTPS.
- There are no mixed content issues (e.g., loading HTTP content on HTTPS pages).
10. Use Google Search Console & Analytics
Regularly monitor your site’s performance and technical health using tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics. These platforms provide valuable insights, including:
- Search performance and impressions
- Crawl errors and security issues
- Site traffic and user behavior
11. Fix Structured Data and Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data that helps search engines understand the content of your site. It can lead to rich snippets in search results and improve your CTR. Check your website for proper schema implementation using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Look for common types of schema:
- Article schema for blog posts
- Product schema for e-commerce sites
- FAQ schema for frequently asked questions pages
12. Analyze Content Quality and Keyword Usage
While this isn’t strictly technical, auditing your content and ensuring proper keyword optimization is a critical aspect of a technical SEO audit.
Check for:
- Content relevance: Does the content meet user intent?
- Keyword targeting: Are you using the right keywords and optimizing for them naturally?
- Content depth and structure: Are pages comprehensive and well-structured with headings, subheadings, and media?
Conclusion
A thorough technical SEO audit involves checking multiple aspects of your website, from its structure and performance to security and user experience. Regularly conducting audits ensures your site remains optimized for both search engines and users. By fixing identified issues and implementing the best practices, you can improve your website’s ranking and overall performance in search results.
